All you need to know about Amazon Route 53
A One-stop DNS Service offered by AWS
Route 53
Definition
AWS Route 53 is simply a domain name service offered by Amazon web services, Its job is to take the user's requested Domain name example: 'aws.amazon.com' and convert into numerical IP address example: "10.72.171.77" and route to the allocated host(EC2) via ELB.
Amazon launched this service in 2010, it supports services that are tightly integrated with AWS, to understand better we need to understand some concepts behind it, below I explained some of the terminologies.
Cloud Terminologies
Regions
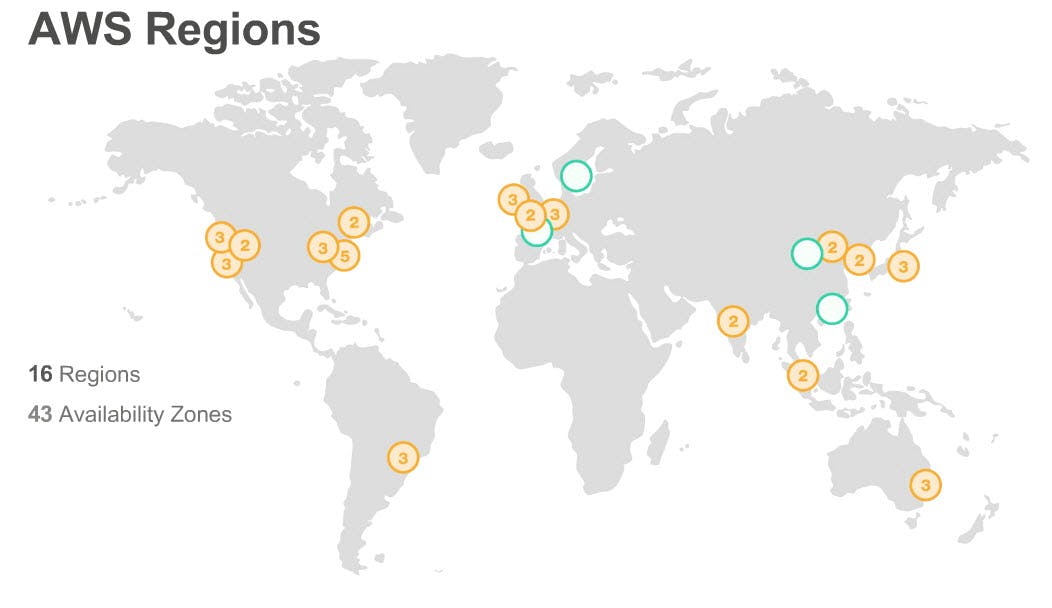
Regions are the physical locations that have multiple clusters of data centers, these locations are foundations for allocating hosts to data transfers the requested resources from the customer, these regions are combined with AZ's
AZ's
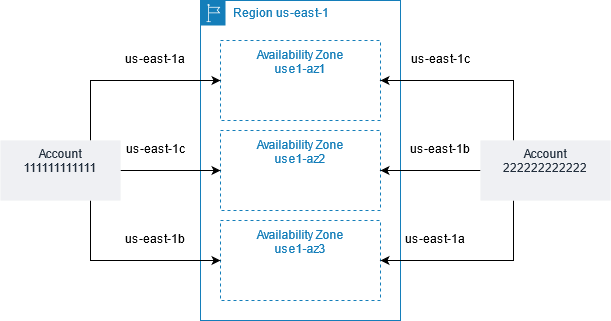
These are called Availability zones which are concise in a particular region, these zones' purpose is to store applications data, multiple AZs are helpful because they can protect our application data from disaster recovery, fault tolerance, single point failure, etc...
Availability zones have a count of a minimum of 3 in a region and a maximum of 6 in a Region
Elastic Compute Cloud

These are also called EC2 Instances which are one of the main blocks of AWS, these are simply servers located in AWS data centers that offer multiple resources, such as storage, compute, and networking.
In the cloud, you may hear of Infrastructure as a service aka IAAS and this is what it is.
S3 Buckets
These are amazon storage services and this is one of the main concepts in AWS, Buckets are referred to as containers that can be designed to store objects.
Objects are simply types of data you store, in S3 everything refers to objects, and S3 is a global service, but you want to create these services region-based.
Bucket names must be unique, because of their usage, and to identify easily, each bucket name assigned to individual AWS customers.
Elastic Load Balancer
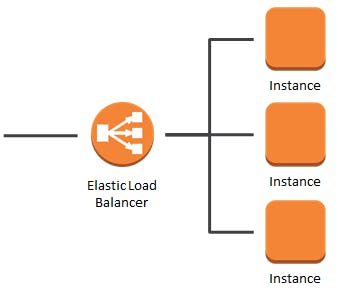
These are called ELB, its purpose is to balance the application load to different EC2 instances Its better use case works under a micro-service architecture (which we see in another article) soon.
When a user requests the website (either static or dynamic) Imagine your application has got 10000 requests per second, the ELB work is to check the healthy EC2 instances and distributed These requests are equally divided among multiple instances.
CloudFront
For info please go through the below article, I clearly explained what CloudFront is.
What is Route 53?

AWS Route 53 is a (Domain name system) web service, which is specially designed to manage cloud applications are hosted on the AWS cloud, and it is route end-users to applications.
which they requested, Route 53 takes the domain name address and converts it into a computer an understandable language called IP address which is a way to identify a specific website that is hosted on the AWS server.
Routing Policies
These are simply a set of guidelines on how to route the requests from the user, we have different types of routing policies that are mostly used.
Types of Routing Policies
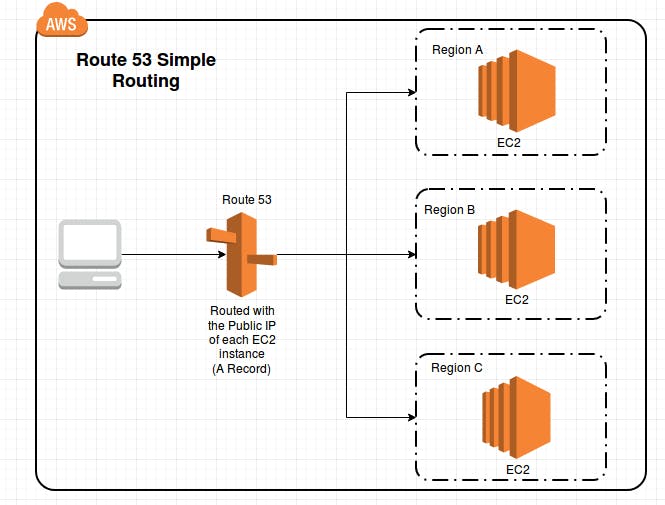
Simple Routing Policy
This works across regions and it is a default routing policy that forwards the routing request without taking the health of the resources into consideration.
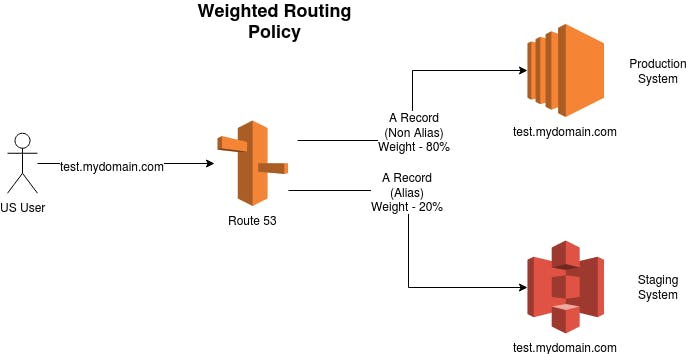
Weighted Routing Policy
It is based on specifications, I mean every instance is weighted( giving a certain percent of requests for each instance ) by you, then these requests go according to your proportions which you weighted.
When testing an application, performing like user acceptance as the application is available to only a few sets of users, want this policy will definitely help.
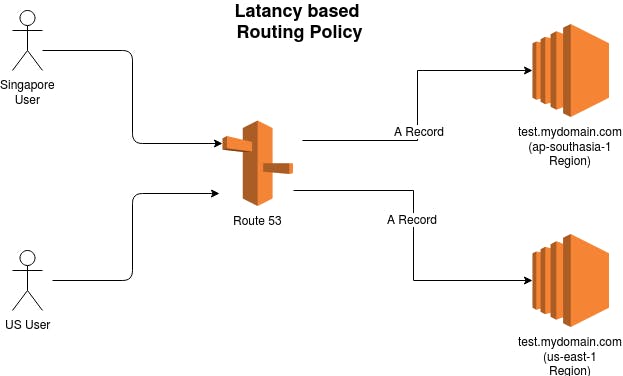
Latency Routing Policy
This works on how fastly the user gets the response back from the resource, it is calculated under what is the best route which takes the fast latency route into consideration.
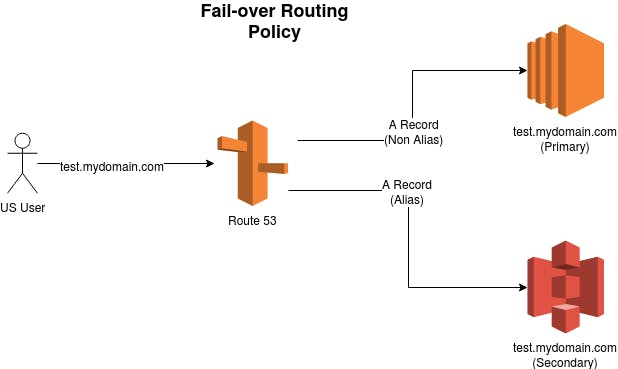
Failover Routing Policy
When the request is going to the primary instance, in case of primary instance may fall it happens in many cases, in that case, it considers a break(fall) of an instance, then this the request is forwarded to a healthy instance
Key Benefits
Traffic Flow
It is an editor where an AWS customer can visualize how the data passes from user to the endpoint is a feature offered by Route-53
We can easily switch back through different policy rules (retrieve back to the previous policy) and it has 4 types of rules which are
- Geo-location
- Latency
- Fail-over
- Weighted
Health Checks
Checks are performed before the traffic entered the resource(instance), If only all checks are passed like fail-over or any other reason, which leads to an un-requested response from the server, It routes the request into a healthy instance.
Alias Records
This is one of the most foundational concepts in Route53, It maps the request to a specific resource while serving the request which resource it wants to go through an example: S3, Cloudfront, DB, etc...
How Does It works?
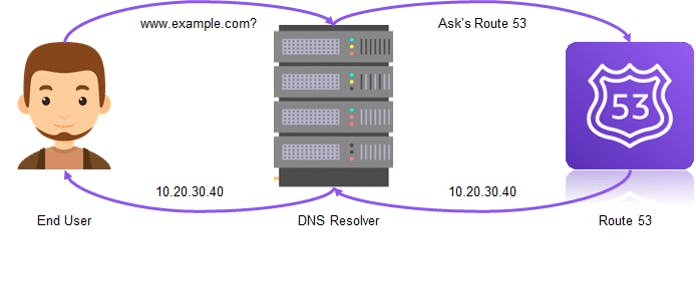
To perform the job, obviously, it wants to go through a series of steps, this happens when a user request access to a web server through Route 53
The user access an address through route 53 that is managed by the host machine here the address is nothing but a website address (google.com)
Next step is managed by the user's ISP or any local network, the user receives the request DNS resolver by Route 53 and the request is forwarded to the root server (consider the the backbone of the internet).
Then the request is forwarded to the TLD aka Top-level-domain by the DNS resolver
The DNS resolver acquires the info from authorized Route 53 4 name servers(translates the domain name into the IP address) which helps to find the requested host, and which resources it wants to be forwarded.
It selects one of the four authorized name servers and requests the resource we need.
This request is acquired by route 53, and sent a request to the DNS, to find the relevant web-page resources that are requested by Route 53, after it successfully finds out its hands the information to the DNS resolver.
Here a TTL (Time to Live) parameter has been attached to the response, after the successful acquisition the data is stored in the local isp cache and in the web browser cache.
The requested web page has been downloaded into a web browser and shows it.
Alternatives to Route 53
Here we have a lot of choices some of them are:
- Google Cloud DNS
- Azure DNS
- Go Daddy premium
- Cloudflare DNS
References
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to connect me on LinkedIn or Twitter, see you with another one. 😊